Baalbek Megaliths: Difference between revisions
(→Religious Claims: added tons of text) |
m (→Other Religious Claims: added more info) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
Most of the claims that have their footing in religion are focused on the Trilithon of the Temple of Jupiter podium. These claims ignore the classical architecture seen at the site in favor of the idea of the podium having Biblical origins. The site was often identified in antiquity as the site of a palace built by King Solomon for the Queen of Sheba. Local legends also claimed that genies were responsible for helping Solomon build the podium because no human workers could have been responsible for the moving of such megalithic stones. This section of the story also explains the Stone of the Pregnant Woman, by claiming that the genies left the stone in the ground as a strike against Solomon for making them work. During the 19th century, it was common for literature to reference Baalbek as such for those who wished to prove the historicity of the Bible. David Urquhart’s work, The Lebanon: A History and a Diary, claimed that the Trilithon had been built in three stages. Two of these stages was before the great Biblical flood, by the claimed exceptional race of men who died during the aforementioned flood. The last stage was completed by Solomon (Starting at Baalbek). Muslim sources follow the same narrative, including that it was the palace of Abraham, or that it was the castle of Solomon built to honor Abraham. There are also others that claim the city is related to the Biblical “Baalath.” (History of Baalbek) | Most of the claims that have their footing in religion are focused on the Trilithon of the Temple of Jupiter podium. These claims ignore the classical architecture seen at the site in favor of the idea of the podium having Biblical origins. The site was often identified in antiquity as the site of a palace built by King Solomon for the Queen of Sheba. Local legends also claimed that genies were responsible for helping Solomon build the podium because no human workers could have been responsible for the moving of such megalithic stones. This section of the story also explains the Stone of the Pregnant Woman, by claiming that the genies left the stone in the ground as a strike against Solomon for making them work. During the 19th century, it was common for literature to reference Baalbek as such for those who wished to prove the historicity of the Bible. David Urquhart’s work, The Lebanon: A History and a Diary, claimed that the Trilithon had been built in three stages. Two of these stages was before the great Biblical flood, by the claimed exceptional race of men who died during the aforementioned flood. The last stage was completed by Solomon (Starting at Baalbek). Muslim sources follow the same narrative, including that it was the palace of Abraham, or that it was the castle of Solomon built to honor Abraham. There are also others that claim the city is related to the Biblical “Baalath.” (History of Baalbek) | ||
==== Other Religious Claims ==== | ==== Other Religious Claims ==== | ||
There are many other religious claims laid on the site, varying greatly across the board. One tells that the podium of Baalbek was the foundation of the Tower of Babel and being built by Nimrod. In a related story from an Arabic manuscript, Baalbek was built under the order of Nimrod when he ruled Lebanon after the flood (History of Baalbek). Another recounts that the site was built by giants who worshipped “the Sun-God” (History of Baalbek). | There are many other religious claims laid on the site, varying greatly across the board. One tells that the podium of Baalbek was the foundation of the Tower of Babel and being built by Nimrod. In a related story from an Arabic manuscript, Baalbek was built under the order of Nimrod when he ruled Lebanon after the flood (History of Baalbek). Istifan Al-Duwayhi has been quoted saying that the site was built but Cain in a “fit of raving madness," and that it was given to his son and then populated by giants after the flood (History of Baalbek). Another recounts that the site was built by giants who worshipped “the Sun-God” (History of Baalbek). | ||
=== Graham Hancock === | === Graham Hancock === | ||
Thank god he has his own blog | Thank god he has his own blog | ||
Revision as of 17:15, 2 December 2019

The Baalbek Megaliths are large megalithic stones located at the site of Baalbek in the Baalbek Valley in Lebanon. The site includes a quarry with large megaliths left still in the ground and the podium of the Temple of Jupiter.[1]
Site History
Baalbek was first excavated in 1898-1903 by a German expedition. The site was ruined, and many expeditions, including some done by the French and Lebanese, reconstructed some of the temple structures during the 1930s, ’50s, and ’60s. The site has been studied since the mid-18th century. The antiquarian Robert Wood wrote The Ruins of Balbec, Otherwise Heliopolis in Coelosyria in 1757, which started the main archaeological interest in the site.[2] The study of the site was interrupted due to the Lebanese civil war from 1975-1990. German expeditions continue to be done on the site, with research focuses on the quarry of Baalbek and the podium of the Temple of Jupiter (Megalith Quarry).
Site Description
The Quarry
The quarry at Baalbek, sometimes referred to as Ḥajjar al-Ḥibla (meaning “The Stone of the Pregnant Woman”), has been the subject of study since antiquity. Recently, more focused research has started, with the German expedition in 2004 being one of the most in-depth. The quarry is the site of all the megalithic stones used at Baalbek, including the Trilithon that makes up the podium of the Temple of Jupiter. It lies about 800 m southeast of the temple complex and consists of four “extraction areas” that provided the megalithic stones of the podium and those left in the ground. Some of the caves left behind from extractions have since been used as burial sites, most likely during the Byzantine era (Abdul).
The Stone of the Pregnant Woman
The Stone of the Pregnant Woman, also referred to as Ḥajjar al-Ḥibla, gives its name to the quarry site of Baalbek. It sits in the extraction area labeled “Area III”, and is 4.2 m x 4.5 m x 21 m in size. The megalith itself shows evidence of tool marks and holes that were most likely used for transportation of the stone from its extraction cave. There is evidence on three of the four sides of working on the stone to smooth the facades.

Area IV Megalith
The megalith at the Area IV extraction area is the second-largest megalith found in the quarry. Its dimensions of 4.6 m x 4.8-5.0 m x 20 m make it larger than the Stone of the Pregnant Woman. The megalith was completely buried in mining debris and was uncovered in the 1970s. It is considered to be a higher quality stone than that of the Stone of the Pregnant Woman and may have been intended to have been part of the podium of the Temple of Jupiter.
Area III Megalith
The megalith at the Area III extraction area is the most recent discovery at the site, as it was uncovered during excavations in 2014. The megalith was uncovered below ground level just to the north of the Stone of the Pregnant Woman, almost underneath it. It measures 5.6 m x 6.1 m x 19.6 m and has several imperfections on some of its facades, including some horizontal cracks and the formation of an imperfection known as karst.
The Temple of Jupiter Platform
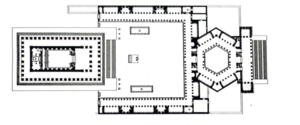
The podium of the Temple of Jupiter is constructed of three megalithic stones known as the Trilithon. These stones are considered to be some of the largest stones used in construction in history. Each of the stones is 4 m x 4 m x 20 m, and weigh about 800 tons.[2] The information on the construction of the podium and thus the temple is foggy. It is relatively considered that construction began in the first century BCE, and finished in the third century CE (Reconstructing Baalbek).
Pesudoarchaeological Claims
Religious Claims
Due to the nature of the uncertainty of the building of the Baalbek temple complex and the megalithic size of the stones, the site has garnered pseudoarchaeological claims on its origin and purpose.
Solomon
Most of the claims that have their footing in religion are focused on the Trilithon of the Temple of Jupiter podium. These claims ignore the classical architecture seen at the site in favor of the idea of the podium having Biblical origins. The site was often identified in antiquity as the site of a palace built by King Solomon for the Queen of Sheba. Local legends also claimed that genies were responsible for helping Solomon build the podium because no human workers could have been responsible for the moving of such megalithic stones. This section of the story also explains the Stone of the Pregnant Woman, by claiming that the genies left the stone in the ground as a strike against Solomon for making them work. During the 19th century, it was common for literature to reference Baalbek as such for those who wished to prove the historicity of the Bible. David Urquhart’s work, The Lebanon: A History and a Diary, claimed that the Trilithon had been built in three stages. Two of these stages was before the great Biblical flood, by the claimed exceptional race of men who died during the aforementioned flood. The last stage was completed by Solomon (Starting at Baalbek). Muslim sources follow the same narrative, including that it was the palace of Abraham, or that it was the castle of Solomon built to honor Abraham. There are also others that claim the city is related to the Biblical “Baalath.” (History of Baalbek)
Other Religious Claims
There are many other religious claims laid on the site, varying greatly across the board. One tells that the podium of Baalbek was the foundation of the Tower of Babel and being built by Nimrod. In a related story from an Arabic manuscript, Baalbek was built under the order of Nimrod when he ruled Lebanon after the flood (History of Baalbek). Istifan Al-Duwayhi has been quoted saying that the site was built but Cain in a “fit of raving madness," and that it was given to his son and then populated by giants after the flood (History of Baalbek). Another recounts that the site was built by giants who worshipped “the Sun-God” (History of Baalbek).
Graham Hancock
Thank god he has his own blog